Disclaimer Privacy Policy
Copyright (c) 2021 Bicuspid Aortic Foundation, All Rights Reserved


Creating a Climate of Hope, an Atmosphere of Caring, and Information for All

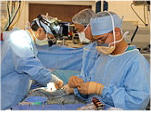
Coarctation Treatment
Life-Saving
Treatment
Coarctation is often treated
in infancy or childhood, but
may also be found in
adults.
Thoracic Aortic Disease (TAD) - What is Aortic Coarctation?
Coarctation or Narrowing of the Aorta
Aortic coarctation means that a section of the aorta is narrow, usually the part of the
descending aorta just past the arch. Statistics vary, but coarctation may be present along
with a bicuspid aortic valv.
It is often found and treated in the early years of life.
It is possible to reach adulthood without symptoms, because other blood vessels take over
some of the blood flow that would normally go through the aorta (collateral circulation).
However, because blood is trying to flow through a narrow opening, pressure may still build
up. This increased pressure in the ascending aorta and its branches to the brain may cause
a break in a fragile vessel in the brain, resulting in bleeding and stroke.
The heart muscle (left ventricle) may also thicken as it pumps against the resistance due to
the narrowed aorta, and could potentially cause diastolic dysfunction or heart failure. Surgery
should be planned before complications such as this happen.


- Aorta
- BAV and Other Heart Valves
- Blood Pressure
- Exercise/Weight Lifting
- Featured Papers
- Guidelines
- Familial TAAD
- History
- Honoring Dr. M.E. Abbott
- Pictures (graphic content)
- Pictures Valvular Strand, Aneurysm (graphic)
- Prosthetic Heart Valves
- Scientific Awards
- Spotlight on Research - Coming Soon
- Video (graphic content)